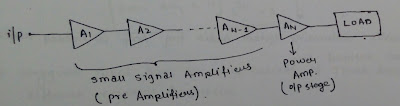
Power amplifier
- It is a large signal amplifier. Due to large signal variation,it has large AC output current and voltage.Hence it can supply large signal power to load.
- Power amplifier can cause harmonic distortion in the output due to non-linerity of transistor.Hence power amplifier should be used at final stage potput stage to keep the distortion minimum.
- A power transistor is used in power
amplifier.
- Power transistor is operated at greater
Ic
and Vce
(Ic
is a few ampere & Vce
is in 10’s of volt).
- Due to greater power dissipation,power
transistor produce greater heat.Hence “Heat sink” should be used to increase
the rate of heat transfer to surroundings (heat sink is made from a good
conductor of Heat such as Aluminimum).
- Performance of power amplifier is measured in terms of conversion efficiency and figure of merit.
 |
| Power amplifier |
.
Conversion
Efficiency:
·
A power amplifier supplies a large AC
power to load because it internally converts a part of DC power drawn from
biasing supply into AC power.
· Conversion Efficiency is a measure of
ability of a power amplifier to convert DC power into AC power.
·
Efficiency = Ac signal power supplied to Load / DC power
drawn from biasing supply
·
% efficiency = Pac / P dc * 100%
2 . Figure
of Merit:
·
It is a ratio of maximum power
dissipation in transistor and maximum AC power which can be supplied to load.
· As power dissipation in transistor is
unwanted, figure of merit (F.O.M.) should be smaller.
·
For ideal power amplifier; F=0 & Efficiency=
100%
·
F = Pd
max. / Pac
max.
Classification
of power amplifier:
According to position of operating point on load
line , amplifiers are divided into 4 type
1 Class-A
2 Class-B
3 Class-AB
4 Class-C
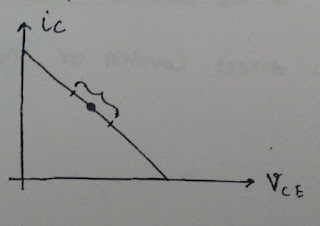
1. Class-A amplifier
:
o An amplifier in which operating point is
approximately in the middle of load line.
o If Q point is at centre of load line
then collector current can have max symmetrical.Hence Class-A amplifier
provide distortion less output.
o When Q-point is at centre of load
line,Quiescent power dissipation will be the highest.Hence in class-A
amplifier power dissipation of transistor is greater (Disadvantage).
 |
| Class-A amplifier |
o
Efficiency= 25% , Vmin = 0
o
Due to low efficiency , Class-A direct
coupled amplifier is not preferred as a power amplifier.
o
Efficiency's is low due to-
- Greater power dissipation in Transistor.
- DC power dissipation in load.
o
Figure Of Merit , F= 2
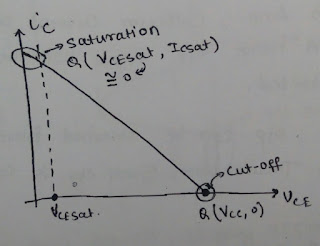
2.Class-B
amplifier :
o
An amplifier in which transistor is operated
either in cut-off region or in saturation region.Operating point is either at
bottom end (or) at top end of load line.
 |
| Class-B amplifier |
o In Class-b amplifier Quiescent power
dissipation is zero i.e. transistor dissipate zero power in absence of AC
input.
Ex: If Q-point in cut-off.
 |
| Q-point in cut-off |
When Q-point in cut-off,collector current can very
only in positive(+) direction.
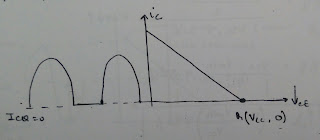
Ex: If Q-point in saturation.
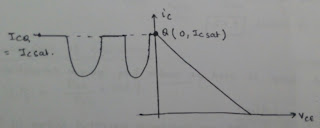 |
| Q-point in saturation |
When Q-point is in saturation ,collector current
can vary only in negative(-) direction.
Application
:
o Class-b push-pull amplifier is used as
untuned power amplifier (or) Audio Frequency power amplifier.
3.Class-AB
power amplifier :
o An amplifier in which operating point is
between Class-A and Class-B position.
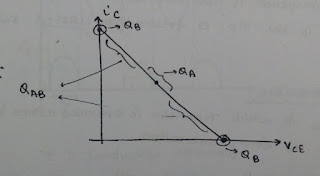 |
| Class-AB power amplifier |
o
Practically, Q-point in Class-AB
amplifier is slightly above cut-off (or) slightly below saturation.
o When Q-point is above cut-off, clipping
occours in Ic waveform during negative cycle and clipping occours in Vce
waveform during positive cycle.
o
Hence output of Class-AB amolifier will
be more than half sinusoidal.
o
Maximum efficiency lies between 50% to
78.5%
o
Power dissipation is less than class-A
but more than class-B.
o
Distortion in output is greater than
class-A but less than class-B.
4.Class-C
power amplifier :
o
An amplifier in which transistor is operated
either in deep cut-off (or) in strong saturation.
o
Deep
cut-off: if Vbe
< Vbe (cut-off)
Vbe (cut-off) is the Vbe value at
which transistor becomes fully OFF. Ic
= Ico
o
Strong
saturation:
Ib
>> I bmin
o Practically , in a class-C amplifier transistor is operated in deep cut-off by applying a negative voltage between base and emitter.
o Practically , in a class-C amplifier transistor is operated in deep cut-off by applying a negative voltage between base and emitter.
o
When Ac input is applied,transistor
remains off in the negative cycle and conducts for a short interval during
positive cycle.
o
Hence output signal of Class-C amplifier
will be less than half sinusoidal.
o
In class-C amplifier has the highest
efficiency (90-100%)
Application:
o
Class-C amplifier is used as Tuned power
amplifier.
Read more>> WLAN
Bluetooth Technology









No comments:
Post a Comment