DIODE
A semiconductor device with two terminals that
conducts current in one direction only.
A diode
just squares current in the reverse course while the reverse voltage is inside
a constrained range generally reverse boundary breaks and the voltage at which
this breakdown happens is called reverse breakdown voltage. The diode goes
about as a valve in the electronic and electrical circuits.
Diode Symbol
The symbol
of a diode is appeared as follows. The sharpened stone focuses toward
traditional current stream in the forward biased condition. That implies the
anode is associated with the p side and cathode is associated with the n side.
 |
| Simple Diode Symbol |
PN Junction Diode Theory
There are
two working regions: P-type and N-type. Also, in light of the connected
voltage, there are three conceivable "biasing" conditions for the P-N
Junction Diode, which are as per the following:
1. Zero
Bias – No outside voltage is connected to the PN intersection diode.
2. Forward
Bias– The voltage potential is associated positively to the P-type terminal
and Negative to the N-type terminal of the Diode.
3. Reverse
Bias– The voltage potential is associated Negative to the P-type terminal
and positively to the N-type terminal of the Diode.
Forward Bias
In the
forward bias condition, the negative terminal of the battery is associated with
the N-type material and the positive terminal of the battery is associated with
the P-Type material. This association is likewise called as giving positive
voltage. Electrons from the N-locale crosses the intersection and enters the
P-area. Because of the alluring power that is created in the P-locale the
electrons are pulled in and move towards the positive terminal. All the while
the openings are pulled in towards the negative terminal of the battery.By the
development of electrons and gaps current streams. In this condition, the width
of the consumption locale diminishes because of the decrease in the quantity of
positive and negative particles.
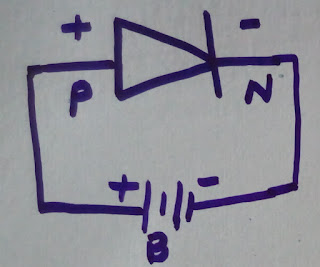 |
| Forward Bias |
Reverse Bias
In the
forward bias condition, the negative terminal of the battery is associated with
the N-type material and the positive terminal of the battery is associated with
the P-type material. This association is otherwise called giving positive
voltage. Henceforth, the electric field because of both the voltage and
consumption layer is a similar way. This makes the electric field more grounded
than previously. Because of this solid electric field, electrons and openings
need more vitality to cross the intersection so they can't diffuse to inverse
area. Consequently, there is no present stream because of absence of
development of electrons and openings.
The
electrons from the N-type semiconductor are pulled in towards the positive
terminal and the gaps from the P-type semiconductor are pulled in towards
negative terminal. This prompts the decrease of the quantity of electrons in
N-type and openings in P-type. Also, positive particles are made in N-type
district and negative particles are made in the P-type locale.
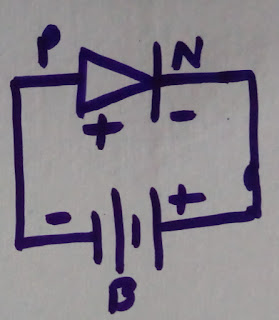 |
| Diode Reverse Bias |
The types of diode include:
1. Zener diode
A Zener diode is a
type of diode that enables current to stream from its anode to its cathode, yet
additionally in the invert direction, when the Zener voltage is come to. Zener
diodes have a profoundly doped p– n intersection.
 |
| Zener Diode |
2. P-N intersection diode
A
pn intersection diode doped at a certain level is a comparison of silicon or
germanium both. Any pentavalent or trivalent contaminations can be added to
shape pn intersection diode. p-n intersection diodes are the electronic parts
that can permit the stream of current just forward way and gives 100 percent
obstruction in switch bearing.
3.Tunnel diode
A passage diode or Esaki diode is a type of
semiconductor diode that has negative opposition because of the quantum
mechanical impact called burrowing. It was created in August 1957 by Leo Esaki,
Yuriko Kurose, and Takashi Suzuki when they were working at Tokyo Tsushin
Kogyo, presently known as Sony.
 |
| Tunnel Diode |
4. Varactor diode
In
hardware, a varicap diode, varactor diode, variable capacitance diode, variable
reactance diode or tuning diode is a sort of diode intended to manhandle the
voltage-subordinate capacitance of a rotate uneven p– n combination.
 |
| Varactor Diode |
5. Schottky diode
These
diodes have a less forward voltage drop, altogether lesser than p-n convergence
diodes. To make them helpful in voltage catching application, the voltage rate
is dropped at a sending current of 1mA is at 0.15V to 0.45V. They are
furthermore used as low mishap rectifier.
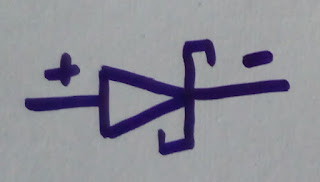 |
| Schottky Diode |
6.Photodiode
A photodiode
is a semiconductor device that changes over light into an electrical flow. The
current is produced when photons are invested in thephotodiode. Photodiodes may
contain optical channels, worked in focal points, and may have vast or little
surface territories.
 |
| Photo Diode |
7.PIN diode
A PIN
diode is a diode with a wide, undoped normal semiconductor territory between a
p-type semiconductor and a n-type semiconductor locale. The p-type and n-type
zones are commonly genuinely doped in light of the way that they are utilized
for ohmic contacts. The wide trademark region is rather than a normal p– n
diode.
8. Laser diode
It is like
a light discharging diode (LED). It utilizes gallium arsenide doped with
components, for example, selenium, aluminum, or silicon to deliver P type and N
type semiconductor materials. While a laser diode has an extra dynamic layer of
undoped (inborn) gallium arsenide have the thickness just a couple of
nanometers, sandwiched between the P and N layers, adequately making a PIN
diode (P type-Intrinsic-N type). It is in this layer the laser light is
created.
 |
| Laser Diode |
9. Avalanche diode
A
torrential slide diode is a diode that is intended to separate and lead at a
predefined turn around inclination voltage. This is to some degree comparable,
yet not indistinguishable to Zener breakdown.
10. Light transmitting diode
Driven is
a shortening of Light Emission Diode, and is a device which produces light by
streaming a current to the p-n intersection like a semiconductor laser (LD). It
emanates different wavelength lights in the bright, noticeable and infrared
districts, comparing to its band hole vitality. Specifically, white LEDs offer
long-life and low vitality utilization contrasted and brilliant lights and
fluorescent lights, and subsequently, are presently progressively utilized for
lighting. White LEDs are additionally utilized for some applications in the zones
of lighting and show, including LCD backdrop illuminations utilized for mobile
phones, traffic lights, street signs, outside showcases, and electric lamps.
 |
| LED symbol |
The P-N junction diode has many
applications
- P-N
intersection diode in reverse biased setup is touchy to light from a range
between 400nm to 1000nm, which incorporates VISIBLE light. In this way, it very
well may be utilized as a photodiode.
- It can
likewise be utilized as a sun based cell.
- P-N
intersection forward bias condition is utilized in all LED lighting
applications.
- The
voltage over the P-N intersection biased is utilized to make Temperature
Sensors, and Reference voltages.
- It is utilized in numerous circuits' rectifiers, varactors for voltage controlled oscillators.
Read more>> WLAN
Bluetooth Technology








